Page 295 - Essential Haematology
P. 295
Chapter 21 Multiple myeloma and related disorders / 281
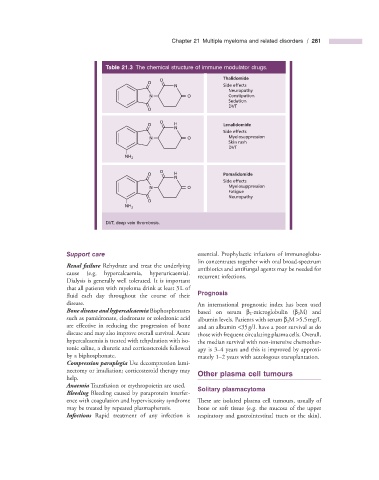
Table 21.3 The chemical structure of immune modulator drugs.
Thalidomide
O O
N Side effects
Neuropathy
N O Constipation
Sedation
DVT
O
O
O H Lenalidomide
N
Side effects
N O Myelosuppression
Skin rash
DVT
NH 2
O
O H Pomalidomide
N
Side effects
N O Myelosuppression
Fatigue
Neuropathy
O
NH 2
DVT, deep vein thrombosis.
Support c are essential. Prophylactic infusions of immunoglobu-
lin concentrates together with oral broad - spectrum
Renal failure Rehydrate and treat the underlying
antibiotics and antifungal agents may be needed for
cause (e.g. hypercalcaemia, hyperuricaemia).
recurrent infections.
Dialysis is generally well tolerated. It is important
that all patients with myeloma drink at least 3 L of
Prognosis
fluid each day throughout the course of their
disease. An international prognostic index has been used
Bone disease and hypercalcaemia Bisphosphonates based on serum β 2 - microglobulin ( β 2 M) and
such as pamidronate, clodronate or zoledronic acid albumin levels. Patients with serum β 2 M > 5.5 mg/L
are effective in reducing the progression of bone and an albumin < 35 g/L have a poor survival as do
disease and may also improve overall survival. Acute those with frequent circulating plasma cells. Overall,
hypercalcaemia is treated with rehydration with iso- the median survival with non - intensive chemother-
tonic saline, a diuretic and corticosteroids followed apy is 3 – 4 years and this is improved by approxi-
by a biphosphonate. mately 1 – 2 years with autologous transplantation.
Compression paraplegia Use decompression lami-
nectomy or irradiation; corticosteroid therapy may Other p lasma c ell t umours
help.
Anaemia Transfusion or erythropoietin are used.
Solitary p lasmacytoma
Bleeding Bleeding caused by paraprotein interfer-
ence with coagulation and hyperviscosity syndrome These are isolated plasma cell tumours, usually of
may be treated by repeated plasmapheresis. bone or soft tissue (e.g. the mucosa of the upper
Infections Rapid treatment of any infection is respiratory and gastrointestinal tracts or the skin).