Page 88 - Essential Haematology
P. 88
74 / Chapter 6 Haemolytic anaemias
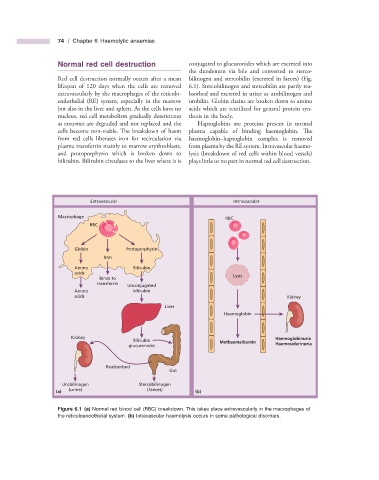
Normal r ed c ell d estruction conjugated to glucuronides which are excreted into
the duodenum via bile and converted to sterco-
Red cell destruction normally occurs after a mean bilinogen and stercobilin (excreted in faeces) (Fig.
lifespan of 120 days when the cells are removed 6.1 ). Stercobilinogen and stercobilin are partly rea-
extravascularly by the macrophages of the reticulo- bsorbed and excreted in urine as urobilinogen and
endothelial (RE) system, especially in the marrow urobilin. Globin chains are broken down to amino
but also in the liver and spleen. As the cells have no acids which are reutilized for general protein syn-
nucleus, red cell metabolism gradually deteriorates thesis in the body.
as enzymes are degraded and not replaced and the Haptoglobins are proteins present in normal
cells become non - viable. The breakdown of haem plasma capable of binding haemoglobin. Th e
from red cells liberates iron for recirculation via haemoglobin – haptoglobin complex is removed
plasma transferrin mainly to marrow erythroblasts, from plasma by the RE system. Intravascular haemo-
and protoporphyrin which is broken down to lysis (breakdown of red cells within blood vessels)
bilirubin. Bilirubin circulates to the liver where it is plays little or no part in normal red cell destruction.
Extravascular Intravascular
Macrophage RBC
RBC
Globin Protoporphyrin
Iron
Amino Bilirubin
acids Lysis
Binds to
transferrin
Unconjugated
Amino bilirubin
acids Kidney
Liver
Haemoglobin
Kidney Haemoglobinuria
Bilirubin Methaemalbumin
glucuronides Haemosiderinuria
Reabsorbed
Gut
Urobilinogen Stercobilinogen
(urine) (faeces)
(a) (b)
Figure 6.1 (a) Normal red blood cell (RBC) breakdown. This takes place extravascularly in the macrophages of
the reticuloendothelial system. (b) Intravascular haemolysis occurs in some pathological disorders.