Page 186 - parasitology for medical and clinical laboratoryprofessionals
P. 186
166 CHAPTER 7
Source: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
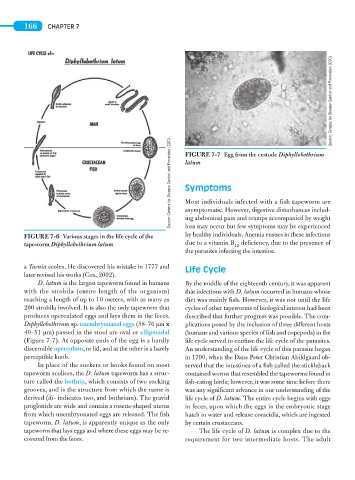
Source: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) FIGURE 7-7 Egg from the cestode Diphyllobothrium
latum
Symptoms
Most individuals infected with a fish tapeworm are
asymptomatic. However, digestive disturbances includ-
loss may occur but few symptoms may be experienced
by healthy individuals. Anemia ensues in these infections
FIGURE 7-6 Various stages in the life cycle of the ing abdominal pain and cramps accompanied by weight
tapeworm Diphyllobothrium latum due to a vitamin B deficiency, due to the presence of
12
the parasites infecting the intestine.
a Taenia scolex. He discovered his mistake in 1777 and Life Cycle
later revised his works (Cox, 2002).
D. latum is the largest tapeworm found in humans By the middle of the eighteenth century, it was apparent
with the strobila (entire length of the organism) that infections with D. latum occurred in humans whose
reaching a length of up to 10 meters, with as many as diet was mainly fish. However, it was not until the life
200 strobila involved. It is also the only tapeworm that cycles of other tapeworms of biological interest had been
produces operculated eggs and lays them in the feces. described that further progress was possible. The com-
Diphyllobothrium sp. unembryonated eggs (58–76 μm x plications posed by the inclusion of three different hosts
40–51 μm) passed in the stool are oval or ellipsoidal (humans and various species of fish and copepods) in the
(Figure 7-7). At opposite ends of the egg is a hardly life cycle served to confuse the life cycle of the parasites.
discernible operculum, or lid, and at the other is a barely An understanding of the life cycle of this parasite began
perceptible knob. in 1790, when the Dane Peter Christian Abildgaard ob-
In place of the suckers or hooks found on most served that the intestines of a fish called the stickleback
tapeworm scolices, the D. latum tapeworm has a struc- contained worms that resembled the tapeworms found in
ture called the bothria, which consists of two sucking fish-eating birds; however, it was some time before there
grooves, and is the structure from which the name is was any significant advance in our understanding of the
derived (di- indicates two, and bothrium). The gravid life cycle of D. latum. The entire cycle begins with eggs
proglottids are wide and contain a rosette-shaped uterus in feces, upon which the eggs in the embryonic stage
from which unembryonated eggs are released. The fish hatch in water and release coracidia, which are ingested
tapeworm, D. latum, is apparently unique as the only by certain crustaceans.
tapeworm that lays eggs and where these eggs may be re- The life cycle of D. latum is complex due to the
covered from the feces. requirement for two intermediate hosts. The adult