Page 712 - Atlas of Histology with Functional Correlations
P. 712
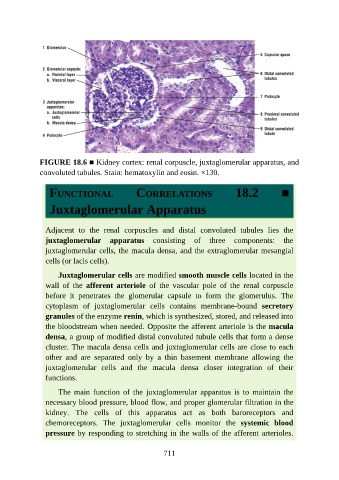
FIGURE 18.6 ■ Kidney cortex: renal corpuscle, juxtaglomerular apparatus, and
convoluted tubules. Stain: hematoxylin and eosin. ×130.
FUNCTIONAL CORRELATIONS 18.2 ■
Juxtaglomerular Apparatus
Adjacent to the renal corpuscles and distal convoluted tubules lies the
juxtaglomerular apparatus consisting of three components: the
juxtaglomerular cells, the macula densa, and the extraglomerular mesangial
cells (or lacis cells).
Juxtaglomerular cells are modified smooth muscle cells located in the
wall of the afferent arteriole of the vascular pole of the renal corpuscle
before it penetrates the glomerular capsule to form the glomerulus. The
cytoplasm of juxtaglomerular cells contains membrane-bound secretory
granules of the enzyme renin, which is synthesized, stored, and released into
the bloodstream when needed. Opposite the afferent arteriole is the macula
densa, a group of modified distal convoluted tubule cells that form a dense
cluster. The macula densa cells and juxtaglomerular cells are close to each
other and are separated only by a thin basement membrane allowing the
juxtaglomerular cells and the macula densa closer integration of their
functions.
The main function of the juxtaglomerular apparatus is to maintain the
necessary blood pressure, blood flow, and proper glomerular filtration in the
kidney. The cells of this apparatus act as both baroreceptors and
chemoreceptors. The juxtaglomerular cells monitor the systemic blood
pressure by responding to stretching in the walls of the afferent arterioles.
711