Page 93 - Deception at work all chapters EBook
P. 93
134 Deception at Work
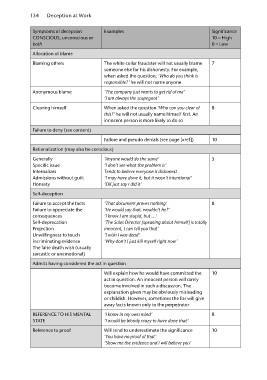
Symptoms of deception Examples Significance
CONSCIOUS, unconscious or 10 = High
both 0 = Low
Allocation of blame
Blaming others The white collar fraudster will not usually blame 7
someone else for his dishonesty. For example,
when asked the question, ‘Who do you think is
responsible?’ he will not name anyone
Anonymous blame ‘The company just wants to get rid of me’
‘I am always the scapegoat’
Clearing himself When asked the question ‘Who can you clear of 8
this?’ he will not usually name himself first. An
innocent person is more likely to do so
Failure to deny (see content)
Failure and pseudo denials (see page [xref]) 10
Rationalization (may also be conscious)
Generally ‘Anyone would do the same’ 5
Specific issue ‘I don’t see what the problem is’
Internalizes Tends to believe everyone is dishonest
Admissions without guilt ‘I may have done it, but it wasn’t intentional’
Honesty ‘OK just say I did it’
Self-deception
Failure to accept the facts ‘That document proves nothing’ 8
Failure to appreciate the ‘He would say that, wouldn’t he?’
consequences ‘I know I am stupid, but …’
Self-deprecation ‘The Sales Director [speaking about himself] is totally
Projection innocent, I can tell you that’
Unwillingness to touch ‘I wish I was dead’
incriminating evidence ‘Why don’t I just kill myself right now’
The false death wish (usually
sarcastic or unemotional)
Admits having considered the act in question
Will explain how he would have committed the 10
act in question. An innocent person will rarely
become involved in such a discussion. The
explanation given may be obviously misleading
or childish. However, sometimes the liar will give
away facts known only to the perpetrator
REFERENCE TO HIS MENTAL ‘I know in my own mind’ 8
STATE ‘I would be bloody crazy to have done that’
Reference to proof Will tend to underestimate the significance 10
‘You have no proof of that’
‘Show me the evidence and I will believe you’