Page 13 - mathematics
P. 13
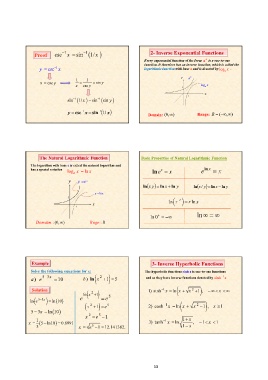
Proof csc1 x sin1 1/ x 2- Inverse Exponential Functions
y csc1 x 1 1 y sin y Every exponential function of the form ax is a one-to-one
x csc
x csc y function. It therefore has an inverse function, which is called the
logarithmic function with base a and is denoted by loga x .
y ax
1 loga x
x
1
sin1 1/ x sin1 sin y Domain: (0,) Range: R (,)
y csc1 x sin11/ x
The Natural Logarithmic Function Basic Properties of Natural Logarithmic Function
The logarithm with base e is called the natural logarithm and ln ex x eln x x
has a special notation loge x ln x lnx y ln x ln y lnx / y ln x ln y
y y ex
1 y lnx ln x r r ln x
1 x
ln 0 ln
Domaim : (0,) Rnge : R
Example 3- Inverse Hyperbolic Functions
Solve the following equations for x: The hyperbolic functions sinh x is one-to-one functions
and so they have inverse functions denoted by sinh1 x
a ) e 53x 10 b ) ln x 2 1 5
1) sinh1 x ln x x 2 1 , x
Solution e ln x 2 1 e 5
x 2 1 e 5
ln e53x ln10 2) cosh1 x ln x x 2 1 , x 1
x 2 e5 1
5 3x ln 10
x e 5 1 12.141382.
x 1 5 ln10 0.8991 3) tanh1 x ln 1 x , 1 x 1
3 1 x
13