Page 320 - Atlas of Small Animal CT and MRI
P. 320
310 Atlas of Small Animal CT and MRI
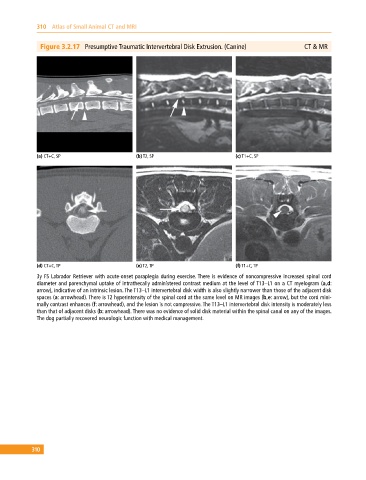
Figure 3.2.17 Presumptive Traumatic Intervertebral Disk Extrusion. (Canine) CT & MR
(a) CT+C, SP (b) T2, SP (c) T1+C, SP
(d) CT+C, TP (e) T2, TP (f) T1+C, TP
3y FS Labrador Retriever with acute‐onset paraplegia during exercise. There is evidence of noncompressive increased spinal cord
diameter and parenchymal uptake of intrathecally administered contrast medium at the level of T13–L1 on a CT myelogram (a,d:
arrow), indicative of an intrinsic lesion. The T13–L1 intervertebral disk width is also slightly narrower than those of the adjacent disk
spaces (a: arrowhead). There is T2 hyperintensity of the spinal cord at the same level on MR images (b,e: arrow), but the cord mini-
mally contrast enhances (f: arrowhead), and the lesion is not compressive. The T13–L1 intervertebral disk intensity is moderately less
than that of adjacent disks (b: arrowhead). There was no evidence of solid disk material within the spinal canal on any of the images.
The dog partially recovered neurologic function with medical management.
310