Page 389 - Feline diagnostic imaging
P. 389
398 23 Liver
Figure 23.38 Transverse oblique ultrasound image of the liver
in a cat presented with icterus, vomiting, and lethargy. The bile
duct is thickened and tortuous, consistent with choledochitis.
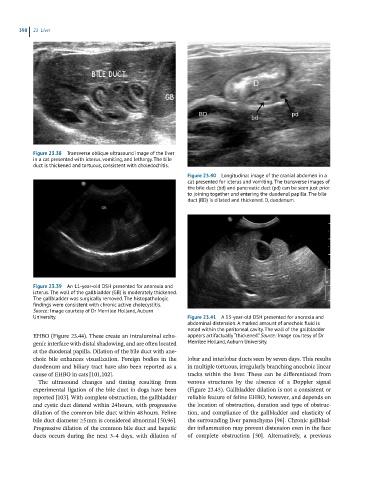
Figure 23.40 Longitudinal image of the cranial abdomen in a
cat presented for icterus and vomiting. The transverse images of
the bile duct (bd) and pancreatic duct (pd) can be seen just prior
to joining together and entering the duodenal papilla. The bile
duct (BD) is dilated and thickened. D, duodenum.
Figure 23.39 An 11-year-old DSH presented for anorexia and
icterus. The wall of the gallbladder (GB) is moderately thickened.
The gallbladder was surgically removed. The histopathologic
findings were consistent with chronic active cholecystitis.
Source: Image courtesy of Dr Merrilee Holland, Auburn
University. Figure 23.41 A 13-year-old DSH presented for anorexia and
abdominal distension. A marked amount of anechoic fluid is
noted within the peritoneal cavity. The wall of the gallbladder
EHBO (Figure 23.44). These create an intraluminal echo- appears artifactually “thickened.” Source: Image courtesy of Dr
genic interface with distal shadowing, and are often located Merrilee Holland, Auburn University.
at the duodenal papilla. Dilation of the bile duct with ane-
choic bile enhances visualization. Foreign bodies in the lobar and interlobar ducts seen by seven days. This results
duodenum and biliary tract have also been reported as a in multiple tortuous, irregularly branching anechoic linear
cause of EHBO in cats [101,102]. tracks within the liver. These can be differentiated from
The ultrasound changes and timing resulting from venous structures by the absence of a Doppler signal
experimental ligation of the bile duct in dogs have been (Figure 23.45). Gallbladder dilation is not a consistent or
reported [103]. With complete obstruction, the gallbladder reliable feature of feline EHBO, however, and depends on
and cystic duct distend within 24 hours, with progressive the location of obstruction, duration and type of obstruc-
dilation of the common bile duct within 48 hours. Feline tion, and compliance of the gallbladder and elasticity of
bile duct diameter 5 mm is considered abnormal [50,96]. the surrounding liver parenchyma [96]. Chronic gallblad-
Progressive dilation of the common bile duct and hepatic der inflammation may prevent distension even in the face
ducts occurs during the next 3–4 days, with dilation of of complete obstruction [50]. Alternatively, a previous