Page 55 - PowerPoint Presentation
P. 55
LOS 36.m: Calculate the value of a capped or READING 36: VALUATION AND ANALYSIS: BONDS WITH EMBEDDED OPTIONS
floored floating-rate bond.
MODULE 36.6: KEY RATE DURATION
A floating-rate bond (“floater”) pays a coupon (in arears but determining at beginning
of the year) that adjusts every period based on an underlying reference rate:
• Capped floater: issuer/borrower caps rate: value of a capped floater = value of a “straight” floater − value of the embedded cap
• Floored floater: investor/lender floors rate: value of a floored floater = value of a “straight” floater + value of the embedded floor
We use the standard backward induction methodology in a BIRT to value these. As with bond valuation with embedded options,
we first adjust the value of the floater at each node to reflect the exercise of an in-the-money option (in this case, a cap or a floor).
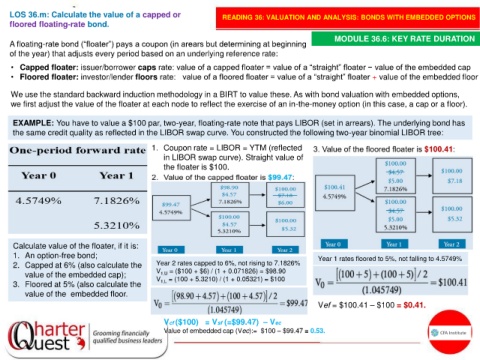
EXAMPLE: You have to value a $100 par, two-year, floating-rate note that pays LIBOR (set in arrears). The underlying bond has
the same credit quality as reflected in the LIBOR swap curve. You constructed the following two-year binomial LIBOR tree:
1. Coupon rate = LIBOR = YTM (reflected
in LIBOR swap curve). Straight value of
the floater is $100.
Calculate value of the floater, if it is:
1. An option-free bond; Year 1 rates floored to 5%, not falling to 4.5749%
2. Capped at 6% (also calculate the Year 2 rates capped to 6%, not rising to 7.1826%
= ($100 + $6) / (1 + 0.071826) = $98.90
value of the embedded cap); V 1,U = (100 + 5.3210) / (1 + 0.05321) = $100
V
3. Floored at 5% (also calculate the 1,L
value of the embedded floor.
Vef = $100.41 – $100 = $0.41.
Vcf ($100) = Vsf (=$99.47) – Vec
Value of embedded cap (Vec):= $100 – $99.47 = 0.53.