Page 578 - Small Animal Internal Medicine, 6th Edition
P. 578
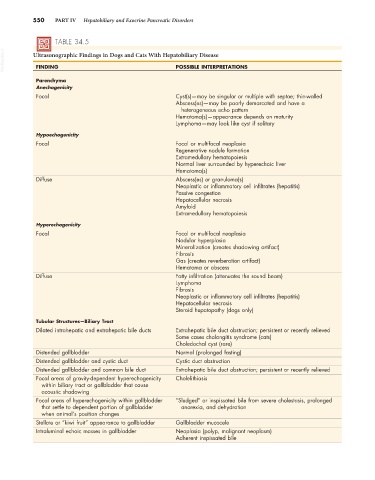
550 PART IV Hepatobiliary and Exocrine Pancreatic Disorders
TABLE 34.5
VetBooks.ir Ultrasonographic Findings in Dogs and Cats With Hepatobiliary Disease
POSSIBLE INTERPRETATIONS
FINDING
Parenchyma
Anechogenicity
Focal Cyst(s)—may be singular or multiple with septae; thin-walled
Abscess(es)—may be poorly demarcated and have a
heterogeneous echo pattern
Hematoma(s)—appearance depends on maturity
Lymphoma—may look like cyst if solitary
Hypoechogenicity
Focal Focal or multifocal neoplasia
Regenerative nodule formation
Extramedullary hematopoiesis
Normal liver surrounded by hyperechoic liver
Hematoma(s)
Diffuse Abscess(es) or granuloma(s)
Neoplastic or inflammatory cell infiltrates (hepatitis)
Passive congestion
Hepatocellular necrosis
Amyloid
Extramedullary hematopoiesis
Hyperechogenicity
Focal Focal or multifocal neoplasia
Nodular hyperplasia
Mineralization (creates shadowing artifact)
Fibrosis
Gas (creates reverberation artifact)
Hematoma or abscess
Diffuse Fatty infiltration (attenuates the sound beam)
Lymphoma
Fibrosis
Neoplastic or inflammatory cell infiltrates (hepatitis)
Hepatocellular necrosis
Steroid hepatopathy (dogs only)
Tubular Structures—Biliary Tract
Dilated intrahepatic and extrahepatic bile ducts Extrahepatic bile duct obstruction; persistent or recently relieved
Some cases cholangitis syndrome (cats)
Choledochal cyst (rare)
Distended gallbladder Normal (prolonged fasting)
Distended gallbladder and cystic duct Cystic duct obstruction
Distended gallbladder and common bile duct Extrahepatic bile duct obstruction; persistent or recently relieved
Focal areas of gravity-dependent hyperechogenicity Cholelithiasis
within biliary tract or gallbladder that cause
acoustic shadowing
Focal areas of hyperechogenicity within gallbladder “Sludged” or inspissated bile from severe cholestasis, prolonged
that settle to dependent portion of gallbladder anorexia, and dehydration
when animal’s position changes
Stellate or “kiwi fruit” appearance to gallbladder Gallbladder mucocele
Intraluminal echoic masses in gallbladder Neoplasia (polyp, malignant neoplasm)
Adherent inspissated bile