Page 579 - Small Animal Internal Medicine, 6th Edition
P. 579
CHAPTER 34 Diagnostic Tests for the Hepatobiliary and Pancreatic System 551
TABLE 34.5
VetBooks.ir Ultrasonographic Findings in Dogs and Cats With Hepatobiliary Disease—cont’d
POSSIBLE INTERPRETATIONS
FINDING
Apparent thickened gallbladder wall Cystic hyperplasia (focal)
Cholecystitis, cholangitis
Infectious canine hepatitis
Hypoalbuminemia with edema formation
Abdominal effusion
Neoplasia
Tubular Structures—Blood Vessels
Dilated hepatic veins and portal veins Right-sided congestive heart failure
Pericardial disease
Intrathoracic caudal vena cava occlusion
Hepatic vein occlusion (Budd-Chiari syndrome)
Prominent hepatic arteries Reduced portal blood flow
Distended portal vein with reduced velocity and flow Portal hypertension of any cause (by Doppler)
with or without hepatofugal flow
Inapparent hepatic vessels Cirrhosis
Severe fatty infiltration
Inapparent portal veins Congenital portosystemic shunt
Portal vein thrombus
Intrahepatic portal vein hypoplasia
Aberrant vessel that communicates with systemic Intrahepatic or extrahepatic congenital portosystemic shunt
circulation
Connection between a portal vein and an artery Arterioportal venous fistula
within one or more liver lobes
Many tortuous veins clustered around left kidney and Acquired portosystemic shunts associated with portal hypertension
along colon
specific for neoplasia, but even hemangiosarcomas may be
missed on US in 15% of cases. Contrast-enhanced US has
been used to improve visualization of small hepatic metas-
tases in dogs. Marolf (2017) has reviewed this and other
advanced imaging modalities in liver disease. Typically,
hepatic lipidosis in cats causes an increase in echogenicity
and so do steroid hepatopathy, diffuse hepatic steatosis, and
diffuse fibrosis (e.g., cirrhosis) in dogs. However, a cirrhotic
liver may also appear normal ultrasonographically.
Dilated anechoic (black) vascular channels and echoic
bile ducts can be identified; biliary tract imaging is particu-
larly useful in cats with suspected biliary tract disease (Fig.
34.11) or dogs and cats with suspected EBDO. The bile duct
can be followed ultrasonographically along its course toward
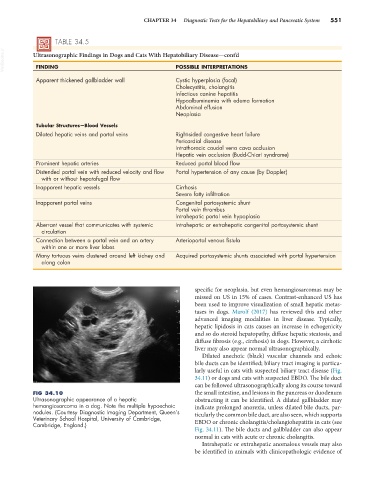
FIG 34.10 the small intestine, and lesions in the pancreas or duodenum
Ultrasonographic appearance of a hepatic obstructing it can be identified. A dilated gallbladder may
hemangiosarcoma in a dog. Note the multiple hypoechoic indicate prolonged anorexia, unless dilated bile ducts, par-
nodules. (Courtesy Diagnostic Imaging Department, Queen’s ticularly the common bile duct, are also seen, which supports
Veterinary School Hospital, University of Cambridge,
Cambridge, England.) EBDO or chronic cholangitis/cholangiohepatitis in cats (see
Fig. 34.11). The bile ducts and gallbladder can also appear
normal in cats with acute or chronic cholangitis.
Intrahepatic or extrahepatic anomalous vessels may also
be identified in animals with clinicopathologic evidence of