Page 165 - Clinical Small Animal Internal Medicine
P. 165
16 Imaging in Cardiovascular Disease 133
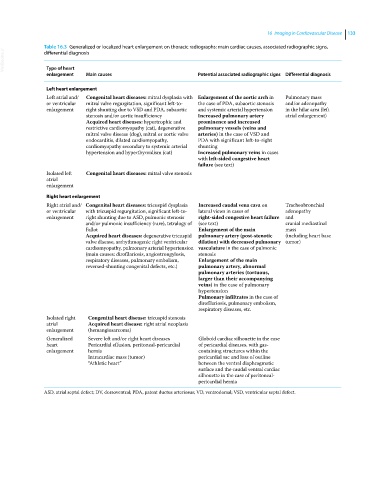
Table 16.3 Generalized or localized heart enlargement on thoracic radiographs: main cardiac causes, associated radiographic signs,
VetBooks.ir
differential diagnosis
Type of heart
enlargement Main causes Potential associated radiographic signs Differential diagnosis
Left heart enlargement
Left atrial and/ Congenital heart diseases: mitral dysplasia with Enlargement of the aortic arch in Pulmonary mass
or ventricular mitral valve regurgitation, significant left‐to‐ the case of PDA, subaortic stenosis and/or adenopathy
enlargement right shunting due to VSD and PDA, subaortic and systemic arterial hypertension in the hilar area (left
stenosis and/or aortic insufficiency Increased pulmonary artery atrial enlargement)
Acquired heart diseases: hypertrophic and prominence and increased
restrictive cardiomyopathy (cat), degenerative pulmonary vessels (veins and
mitral valve disease (dog), mitral or aortic valve arteries) in the case of VSD and
endocarditis, dilated cardiomyopathy, PDA with significant left‐to‐right
cardiomyopathy secondary to systemic arterial shunting
hypertension and hyperthyroidism (cat) Increased pulmonary veins in cases
with left‐sided congestive heart
failure (see text)
Isolated left Congenital heart diseases: mitral valve stenosis
atrial
enlargement
Right heart enlargement
Right atrial and/ Congenital heart diseases: tricuspid dysplasia Increased caudal vena cava on Tracheobronchial
or ventricular with tricuspid regurgitation, significant left‐to‐ lateral views in cases of adenopathy
enlargement right shunting due to ASD, pulmonic stenosis right‐sided congestive heart failure and
and/or pulmonic insufficiency (rare), tetralogy of (see text) cranial mediastinal
Fallot Enlargement of the main mass
Acquired heart diseases: degenerative tricuspid pulmonary artery (post‐stenotic (including heart base
valve disease, arrhythmogenic right ventricular dilation) with decreased pulmonary tumor)
cardiomyopathy, pulmonary arterial hypertension vasculature in the case of pulmonic
(main causes: dirofilariosis, angiostrongylosis, stenosis
respiratory diseases, pulmonary embolism, Enlargement of the main
reversed‐shunting congenital defects, etc.) pulmonary artery, abnormal
pulmonary arteries (tortuous,
larger than their accompanying
veins) in the case of pulmonary
hypertension
Pulmonary infiltrates in the case of
dirofilariosis, pulmonary embolism,
respiratory diseases, etc.
Isolated right Congenital heart disease: tricuspid stenosis
atrial Acquired heart disease: right atrial neoplasia
enlargement (hemangiosarcoma)
Generalized Severe left and/or right heart diseases Globoid cardiac silhouette in the case
heart Pericardial effusion, peritoneal‐pericardial of pericardial diseases, with gas‐
enlargement hernia containing structures within the
Intracardiac mass (tumor) pericardial sac and loss of outline
“Athletic heart” between the ventral diaphragmatic
surface and the caudal ventral cardiac
silhouette in the case of peritoneal‐
pericardial hernia
ASD, atrial septal defect; DV, dorsoventral; PDA, patent ductus arteriosus; VD, ventrodorsal; VSD, ventricular septal defect.