Page 411 - Atlas of Histology with Functional Correlations
P. 411
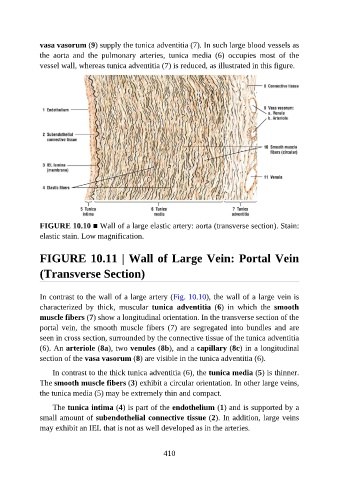
vasa vasorum (9) supply the tunica adventitia (7). In such large blood vessels as
the aorta and the pulmonary arteries, tunica media (6) occupies most of the
vessel wall, whereas tunica adventitia (7) is reduced, as illustrated in this figure.
FIGURE 10.10 ■ Wall of a large elastic artery: aorta (transverse section). Stain:
elastic stain. Low magnification.
FIGURE 10.11 | Wall of Large Vein: Portal Vein
(Transverse Section)
In contrast to the wall of a large artery (Fig. 10.10), the wall of a large vein is
characterized by thick, muscular tunica adventitia (6) in which the smooth
muscle fibers (7) show a longitudinal orientation. In the transverse section of the
portal vein, the smooth muscle fibers (7) are segregated into bundles and are
seen in cross section, surrounded by the connective tissue of the tunica adventitia
(6). An arteriole (8a), two venules (8b), and a capillary (8c) in a longitudinal
section of the vasa vasorum (8) are visible in the tunica adventitia (6).
In contrast to the thick tunica adventitia (6), the tunica media (5) is thinner.
The smooth muscle fibers (3) exhibit a circular orientation. In other large veins,
the tunica media (5) may be extremely thin and compact.
The tunica intima (4) is part of the endothelium (1) and is supported by a
small amount of subendothelial connective tissue (2). In addition, large veins
may exhibit an IEL that is not as well developed as in the arteries.
410