Page 225 - Feline diagnostic imaging
P. 225
228 13 Acquired Heart Disease
(b)
(a)
(c)
(d)
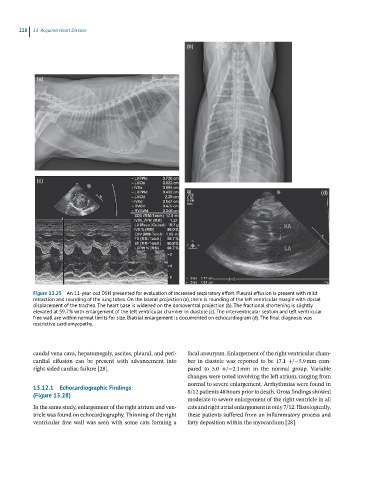
Figure 13.25 An 11-year-old DSH presented for evaluation of increased respiratory effort. Pleural effusion is present with mild
retraction and rounding of the lung lobes. On the lateral projection (a), there is rounding of the left ventricular margin with dorsal
displacement of the trachea. The heart base is widened on the dorsoventral projection (b). The fractional shortening is slightly
elevated at 59.7% with enlargement of the left ventricular chamber in diastole (c). The interventricular septum and left ventricular
free wall are within normal limits for size. Biatrial enlargement is documented on echocardiogram (d). The final diagnosis was
restrictive cardiomyopathy.
caudal vena cava, hepatomegaly, ascites, pleural, and peri focal aneurysm. Enlargement of the right ventricular cham
cardial effusion can be present with advancement into ber in diastole was reported to be 17.1 +/−5.9 mm com
right‐sided cardiac failure [28]. pared to 5.0 +/−2.1 mm in the normal group. Variable
changes were noted involving the left atrium, ranging from
13.12.1 Echocardiographic Findings normal to severe enlargement. Arrhythmias were found in
(Figure 13.28) 8/12 patients 48 hours prior to death. Gross findings showed
moderate to severe enlargement of the right ventricle in all
In the same study, enlargement of the right atrium and ven cats and right atrial enlargement in only 7/12. Histologically,
tricle was found on echocardiography. Thinning of the right these patients suffered from an inflammatory process and
ventricular free wall was seen with some cats forming a fatty deposition within the myocardium [28].